|
|
|
Publication 15
|
Repayment of prior year wages. If you receive repayments for wages paid during a prior year, report an adjustment on the Form 941 for the quarter during which the repayment was made to recover the social security and Medicare taxes. Instead of making an adjustment on Form 941, you may file a claim for these taxes using Form 843. You may not make an adjustment for income tax withholding because the wages were paid during a prior year.

Prior Period Adjustment Example
You also must file Forms W-2c and W-3c with the SSA to correct social security and Medicare wages and taxes. Do not correct wages (box 1) on Form W-2c for the amount paid in error. Give a copy of Form W-2c to the employee.
Note: The wages paid in error in the prior year remain taxable to the employee for that year. This is because the employee received and had use of those funds during that year. The employee is not entitled to file an amended return (Form 1040X) to recover the income tax on these wages. Instead, the employee is entitled to a deduction (or credit in some cases) for the repaid wages on his or her income tax return for the year of repayment.
The Federal Unemployment Tax Act (FUTA), with state unemployment systems, provides for payments of unemployment compensation to workers who have lost their jobs. Most employers pay both a Federal and a state unemployment tax. A list of state unemployment tax agencies, including addresses and phone numbers, is available in Pub. 926, Household Employer's Tax Guide. Only the employer pays FUTA tax; it is not withheld from the employee's wages. For more information, see the Instructions for Form 940.
Note: Services rendered after December 20, 2000, to a federally recognized Indian tribal government (or any subdivision, subsidiary, or business wholly owned by such an Indian tribe) are exempt from FUTA tax, subject to the tribe's compliance with state law. For more information, see Announcement 2001-16 and Code section 3309(d). You can find Announcement 2001-16 on page 715 of Internal Revenue Bulletin 2001-8, at www.irs.gov/bus_info/bullet.html.
Use the following three tests to determine whether you must pay FUTA tax. Each test applies to a different category of employee, and each is independent of the others. If a test describes your situation, you are subject to FUTA tax on the wages you pay to employees in that category during the current calendar year.
You are subject to FUTA tax in 2003 on the wages you pay employees who are not farmworkers or household workers if in the current or preceding calendar year:
You are subject to FUTA tax only if you paid total cash wages of $1,000 or more (for all household employees) in any calendar quarter in 2002 or 2003. A household worker is an employee who performs household work in a private home, local college club, or local fraternity or sorority chapter.
You are subject to FUTA tax on the wages you pay to farmworkers if:
Computing FUTA tax. For 2002 and 2003, the FUTA tax rate is 6.2%. The tax applies to the first $7,000 you pay each employee as wages during the year. The $7,000 is the Federal wage base. Your state wage base may be different. Generally, you can take a credit against your FUTA tax for amounts you paid into state unemployment funds. This credit cannot be more than 5.4% of taxable wages. If you are entitled to the maximum 5.4% credit, the FUTA tax rate after the credit is 0.8%.
Successor employer. If you acquired a business from an employer who was liable for FUTA tax, you may be able to count the wages that employer paid to the employees who continue to work for you when you figure the $7,000 FUTA wage base. See the Instructions for Form 940.
Depositing FUTA tax. For deposit purposes, figure FUTA tax quarterly. Determine your FUTA tax liability by multiplying the amount of wages paid during the quarter by .008 (0.8%). Stop depositing FUTA tax on an employee's wages when he or she reaches $7,000 in wages for the calendar year. If any part of the wages subject to FUTA are exempt from state unemployment tax, you may have to deposit more than the tax using the 0.8% rate. For example, in certain states, wages paid to corporate officers, certain payments of sick pay by unions, and certain fringe benefits, are exempt from state unemployment tax.
If your FUTA tax liability for a quarter is $100 or less, you do not have to deposit the tax. Instead, you may carry it forward and add it to the liability figured in the next quarter to see if you must make a deposit. If your FUTA tax liability for any calendar quarter in 2003 is over $100 (including any FUTA tax carried forward from an earlier quarter), you must deposit the tax by electronic funds transfer (EFTPS) or in an authorized financial institution using Form 8109, Federal Tax Deposit Coupon. See section 11 for information on these two deposit methods.
Note: You are not required to deposit FUTA taxes for household employees unless you report their wages on Form 941 or 943. See Pub. 926, Household Employer's Tax Guide, for more information.
When to deposit. Deposit the FUTA tax by the last day of the first month that follows the end of the quarter.
If your liability for the fourth quarter (plus any undeposited amount from any earlier quarter) is over $100, deposit the entire amount by the due date of Form 940 or Form 940-EZ (January 31). If it is $100 or less, you can either make a deposit or pay the tax with your Form 940 or 940-EZ by January 31.
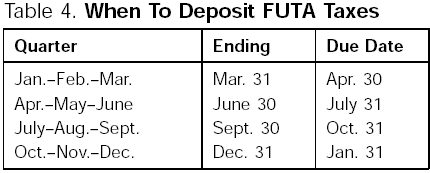
When To Deposit FUTA Taxes
Reporting FUTA tax. Use Form 940 or 940-EZ, Employer's Annual Federal Unemployment (FUTA) Tax Return, to report this tax. The IRS will mail a preaddressed Form 940 or 940-EZ to you if you filed a return the year before. If you do not receive Form 940 or 940-EZ, you can get the form by calling 1-800-TAX-FORM (1-800-829-3676).
Form 940-EZ requirements. You may be able to use Form 940-EZ instead of Form 940 if (1) you paid unemployment taxes (contributions) to only one state, (2) you paid state unemployment taxes by the due date of Form 940 or 940-EZ, and (3) all wages that were taxable for FUTA tax purposes were also taxable for your state's unemployment tax. For example, if you paid wages to corporate officers (these wages are subject to FUTA tax) in a state that exempts these wages from its unemployment taxes, you cannot use Form 940-EZ.