34. Credit for the Elderly or the Disabled
Introduction
If you qualify, the law provides a number of credits that can reduce the tax you owe
for a year. One of these credits is the credit for the elderly or the disabled.
This chapter explains:
- Who qualifies for the credit for the elderly or the disabled, and
- How to figure this credit.
You may be able to take this credit if you are:
- Age 65 or older, or
- Retired on permanent and total disability.
Useful Items
You may want to see:
Publication
- 524 Credit for the Elderly or the Disabled
- 554 Older Americans' Tax Guide
- 967 The IRS Will Figure Your Tax
Forms (and Instructions)
- Schedule 3 (Form 1040A) Credit for the Elderly or the Disabled for Form
1040A Filers
- Schedule R (Form 1040) Credit for the Elderly or the Disabled
Can You Take
the Credit?
You can take the credit for the elderly or the disabled if you meet both
of the following requirements.
- You are a qualified individual.
- Your income is not more than certain limits.
You can use Figure 34-A and Figure 34-B as guides to see if you
qualify.
Use Figure 34-A first to see if you are a qualified individual. If you are, go
to Figure 34-B to make sure your income is not too high to take the credit.
 You can take the
credit only if you file Form 1040 or Form 1040A. You cannot take the credit if you file
Form 1040EZ. You can take the
credit only if you file Form 1040 or Form 1040A. You cannot take the credit if you file
Form 1040EZ.
Qualified Individual
You are a qualified individual for this credit if you are a U.S. citizen or resident
and either of the following applies.
- You were age 65 or older at the end of 2002.
- You were under age 65 at the end of 2002 and all three of the following statements are
true.
- You retired on permanent and total disability (explained later).
- You received taxable disability income for 2002.
- On January 1, 2002, you had not reached mandatory retirement age (defined later under Disability
income).
Age 65. You are considered to be age 65 on the day before your 65th
birthday. Therefore, you are 65 at the end of the year if your 65th birthday is on January
1 of the following year.
U.S. Citizen or Resident
You must be a U.S. citizen or resident (or be treated as a resident) to take the
credit. Generally, you cannot take the credit if you were a nonresident alien at any time
during the tax year.
Exceptions. You may be able to take the credit if you are a
nonresident alien who is married to a U.S. citizen or resident at the end of the tax year
and you and your spouse choose to treat you as a U.S. resident. If you make that choice,
both you and your spouse are taxed on your worldwide income.
If you were a nonresident alien at the beginning of the year and a resident at the end
of the year, and you were married to a U.S. citizen or resident at the end of the year,
you may be able to choose to be treated as a U.S. resident for the entire year. In that
case, you may be allowed to take the credit. For information on these choices, see chapter
1 of Publication 519, U.S. Tax Guide for Aliens.
Married Persons
Generally, if you are married at the end of the tax year, you and your spouse must file
a joint return to take the credit. However, if you and your spouse did not live in the
same household at any time during the tax year, you can file either joint or separate
returns and still take the credit.
Head of household. You can file as head of household and qualify to
take the credit, even if your spouse lived with you during the first 6 months of the year,
if you meet all the tests. See Head of Household in chapter 2 for the tests you
must meet.
Under Age 65
If you are under age 65, you can qualify for the credit only if you are retired on
permanent and total disability. If you retired after January 1, 1977, you are retired on
permanent and total disability if you were permanently and totally disabled when you
retired.
Even if you do not retire formally, you are considered retired on disability when you
have stopped working because of your disability.
Permanent and total disability. You are permanently and totally disabled if you cannot engage in any
substantial gainful activity because of your physical or mental condition. A
physician must certify that the condition has lasted or can be expected to last
continuously for 12 months or more, or that the condition can be expected to result in
death. See Physician's statement, later.
Substantial gainful activity. Substantial gainful activity
is the performance of significant duties over a reasonable period of time while working
for pay or profit, or in work generally done for pay or profit.
Full-time work (or part-time work done at your employer's convenience) in a competitive
work situation for at least the minimum wage conclusively shows that you are able to
engage in substantial gainful activity.
Substantial gainful activity is not work you do to take care of yourself or your home.
It is not unpaid work on hobbies, institutional therapy or training, school attendance,
clubs, social programs, and similar activities. However, doing this kind of work may show
that you are able to engage in substantial gainful activity.
The fact that you have not worked for some time is not, of itself, conclusive evidence
that you cannot engage in substantial gainful activity.
Sheltered employment. Certain work offered at qualified
locations to physically or mentally impaired persons is considered sheltered employment.
These qualified locations are in sheltered workshops, hospitals and similar institutions,
homebound programs, and Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) sponsored homes.
Compared to commercial employment, pay is lower for sheltered employment. Therefore,
one usually does not look for sheltered employment if he or she can get other employment.
The fact that one has accepted sheltered employment is not proof of that person's ability
to engage in substantial gainful activity.
Physician's statement. If you are under age 65, you must have your
physician complete a statement certifying that you were permanently and totally disabled
on the date you retired. You can use the statement in the instructions for Schedule R
(Form 1040) or Schedule 3 (Form 1040A).
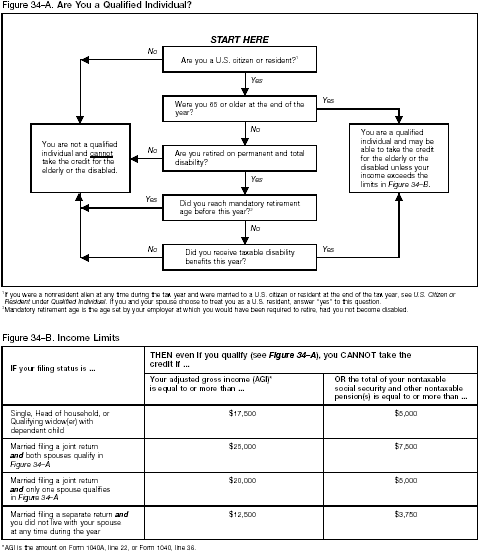
Figure 34-A Are You a Qualified Individual? Figure 34-B Income Limits
You do not have to file this statement with your Form 1040 or Form 1040A, but you must
keep it for your records.
Veterans. If the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA)
certifies that you are permanently and totally disabled, you can substitute VA Form
21-0172, Certification of Permanent and Total Disability, for the physician's
statement you are required to keep. VA Form 21-0172 must be signed by a person authorized
by the VA to do so. You can get this form from your local VA regional office.
Physician's statement obtained in earlier year. If you got
a physician's statement in an earlier year and, due to your continued
disabled condition, you were unable to engage in any substantial gainful activity during
2002, you may not need to get another physician's statement for 2002. For a detailed
explanation of the conditions you must meet, see the instructions for Part II of Schedule
R (Form 1040) or Schedule 3 (Form 1040A). If you meet the required conditions, check the
box on line 2 of Part II of Schedule R (Form 1040) or Schedule 3 (Form 1040A).
If you checked box 4, 5, or 6 in Part I of either Schedule R or Schedule 3, print in
the space above the box on line 2 in Part II, the first name(s) of the spouse(s) for whom
the box is checked.
Disability income. If you are
under age 65, you can qualify for the credit only if you have taxable disability income.
Disability income must meet both of the following requirements.
- It must be paid under your employer's accident or health plan or pension plan.
- It must be included in your income as wages (or payments instead of wages) for the time
you are absent from work because of permanent and total disability.
Payments that are not disability income. Any payment you
receive from a plan that does not provide for disability retirement is not disability
income. Any lump-sum payment for accrued annual leave that you receive when you retire on
disability is a salary payment and is not disability income.
For purposes of the credit for the elderly or the disabled,
disability income does not include amounts you receive after you reach mandatory
retirement age. Mandatory retirement age is the age set by your employer
at which you would have had to retire, had you not become disabled.
Income Limits
To determine if you can claim the credit, you must consider two income limits. The
first limit is the amount of your adjusted gross income (AGI). The second limit is the
amount of nontaxable social security and other nontaxable pensions you received. The
limits are shown in Figure 34-B, earlier.
If both your AGI and nontaxable pensions are less than the income limits, you may be
able to claim the credit. See Figuring the Credit, next.
 If either your
AGI or your nontaxable pensions are equal to or more than the income
limits, you cannot take the credit. If either your
AGI or your nontaxable pensions are equal to or more than the income
limits, you cannot take the credit.
Figuring the Credit
You can figure the credit yourself (see the explanation that follows) or the IRS will
figure it for you. See Credit Figured for You, later.
Figuring the credit yourself. If
you figure the credit yourself, fill out the front of either Schedule R (if you are filing
Form 1040) or Schedule 3 (if you are filing Form 1040A). Next, fill out Part III of
either Schedule R or Schedule 3.
Table 34-1. Initial Amounts
|
IF your filing status is ... |
|
THEN enter on line 10 of Schedule R (Form 1040)
or Schedule 3 (Form 1040A)... |
|
Single, head of household, or a qualifying widow(er) with dependent
child and, by the end of 2002, you were |
|
|
|
|
· 65 or older |
$5,000 |
|
|
· under 65 and retired on permanent and
total disability 1 |
$5,000 |
|
Married filing a joint return and by the end of 2002 |
|
|
|
|
· both of you were 65 or older |
$7,500 |
|
|
· both of you were under 65 and one of you retired on permanent and total
disability 1 |
$5,000 |
|
|
· both of you were under 65 and both of you retired on permanent and
total disability 2 |
$7,500 |
|
|
· one of you was 65 or older, and the other was under 65 and retired on
permanent and total disability 3 |
$7,500 |
|
|
· one of you was 65 or older, and the
other was under 65 and not retired on permanent and total disability |
$5,000 |
|
Married filing a separate return and you did not live with your
spouse at any time during the year and, by the end of 2002, you were |
|
|
|
|
· 65 or older |
$3,750 |
|
|
· under 65 and retired on permanent and total disability 1 |
$3,750 |
| 1Amount cannot be more than the taxable disability income. |
|
| 2Amount cannot be more than your combined taxable disability income. |
|
| 3Amount is $5,000 plus the taxable disability income of the spouse under
age 65, but not more than $7,500. |
|
 There are four
steps in Part III to determine the amount of your credit: There are four
steps in Part III to determine the amount of your credit:
- Determine your initial amount (lines 10-12).
- Total any nontaxable social security and certain other nontaxable
pensions and disability benefits you received (lines 13a, 13b, and 13c).
- Determine your excess adjusted gross income ( lines 14-17).
- Determine your credit (lines 18-24 of Schedule R or lines 18-22 of Schedule 3).
These steps are discussed in more detail next.
Step 1. Determine Initial Amount
To figure the credit, you must first determine your initial amount. See Table 34-1.
Initial amounts for persons under age 65. If you are a qualified
individual under age 65, your initial amount cannot be more than your taxable disability
income.
Step 2. Total Certain Nontaxable Pensions and Benefits
Step 2 is to figure the total amount of nontaxable social security and certain other
nontaxable payments you received during the year. (See Nontaxable payments,
later.)
Enter these nontaxable payments on lines 13a or 13b, and total them on line 13c. If you
are married filing a joint return, you must enter the combined amount of nontaxable
payments both you and your spouse receive.
 Worksheets are
provided in the Form 1040 or Form 1040A instructions to help you determine if any part of
your social security benefits (or equivalent railroad retirement benefits) is taxable. Worksheets are
provided in the Form 1040 or Form 1040A instructions to help you determine if any part of
your social security benefits (or equivalent railroad retirement benefits) is taxable.
Nontaxable payments. Include the following nontaxable payments in
the amounts you enter on lines 13a and 13b.
- Nontaxable social security payments. This is the nontaxable part of the amount of
benefits shown in box 5 of Form SSA-1099, which includes disability benefits, before
deducting any amounts withheld to pay premiums on supplementary Medicare insurance, and
before any reduction because of receipt of a benefit under workers' compensation.
Do
not include a lump-sum death benefit payment you may receive as a surviving spouse, or a
surviving child's insurance benefit payment you may receive as a guardian.
- Social security equivalent part of tier 1 railroad retirement pension payments that is
not taxed. This is the nontaxable part of the amount of benefits shown in box 5 of Form
RRB-1099.
- Nontaxable pension or annuity payments or disability benefits that are paid under a law
administered by the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA).
Do not include amounts
received as a pension, annuity, or similar allowance for personal injuries or sickness
resulting from active service in the armed forces of any country or in the National
Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration or the Public Health Service, or as a disability
annuity under section 808 of the Foreign Service Act of 1980.
- Pension or annuity payments or disability benefits that are excluded from income under
any provision of federal law other than the Internal Revenue Code.
Do not include
amounts that are a return of your cost of a pension or annuity. These amounts do not
reduce your initial amount.
 You should be
sure to take into account all of the nontaxable amounts you receive. These amounts are
verified by the IRS through information supplied by other government agencies. You should be
sure to take into account all of the nontaxable amounts you receive. These amounts are
verified by the IRS through information supplied by other government agencies.
Step 3. Determine Excess
Adjusted Gross Income
You also must reduce your initial amount by your excess adjusted gross income. Figure
your excess adjusted gross income on lines 14 through 17.
You figure your excess adjusted gross income as follows:
- Subtract from your adjusted gross income (line 36 of Form 1040 or line 22 of Form 1040A)
the amount shown for your filing status in the following list:
- $7,500 if you are single, a head of household, or a qualifying widow(er) with a
dependent child,
- $10,000 if you are married filing a joint return, or
- $5,000 if you are married filing a separate return and you and your spouse did
not live in the same household at any time during the tax year.
- Divide the result of (1) by 2.
Step 4. Determine Your Credit
To determine if you can take the credit, you must add the amounts you figured in Step 2
and Step 3.
| IF the total of Steps 2
and 3 is ... |
|
THEN ... |
| Equal to or more than
the amount in Step 1 |
|
You cannot take the credit. |
| Less than the amount
in Step 1 |
|
You can take the credit. |
Figuring the credit. If you can take the credit, subtract the total
of Step 2 and Step 3 from the amount in Step 1 and multiply the result by 15%. This is
your credit.
In certain cases, the amount of your credit may be limited. See Limit on credit,
later.
Example. You are 66 years old and your spouse is 64. Your spouse
is not disabled. You file a joint return on Form 1040. Your adjusted gross income is
$14,630. Together you received $3,200 from social security, which was nontaxable. You
figure the credit as follows:
| 1) |
Initial amount |
|
$5,000 |
| 2) |
Subtract the total of: |
|
|
|
|
|
a) Nontaxable social security and other nontaxable pensions |
|
$3,200 |
|
|
|
b) Excess adjusted gross income [($14,630 - $10,000) ÷ 2] |
|
2,315 |
|
5,515 |
| 3) |
Balance (Not less than -0-) |
|
-0- |
| 4) |
Credit |
|
-0- |
You cannot take the credit since your nontaxable social security (line 2a) plus your
excess adjusted gross income (line 2b) is more than your amount on line 1.
Limit on credit. The amount of credit you can claim may be limited
if any of the following apply.
- You file Form 1040A and the credit you figured on line 20 of Schedule 3 is more than the
tax on Form 1040A, line 28.
- You file Form 1040 and the credit you figured on line 20 of Schedule R is more than the
amount on Form 1040, line 44 (regular tax plus any alternative minimum tax), minus any
foreign tax credit on Form 1040, line 45.
- You are claiming the credit for child and dependent care expenses on:
- Form 1040A, line 29, or
- Form 1040, line 46.
Figure any limit on your credit on lines 21-24 of Schedule R or lines 21-22 of Schedule
3.
- Continue - |
 There are four
steps in Part III to determine the amount of your credit:
There are four
steps in Part III to determine the amount of your credit:  Worksheets are
provided in the Form 1040 or Form 1040A instructions to help you determine if any part of
your social security benefits (or equivalent railroad retirement benefits) is taxable.
Worksheets are
provided in the Form 1040 or Form 1040A instructions to help you determine if any part of
your social security benefits (or equivalent railroad retirement benefits) is taxable.  You should be
sure to take into account all of the nontaxable amounts you receive. These amounts are
verified by the IRS through information supplied by other government agencies.
You should be
sure to take into account all of the nontaxable amounts you receive. These amounts are
verified by the IRS through information supplied by other government agencies.